 In 1940, fewer than one in twenty Americans had a college degree. Now it’s better than one in four[1]. Fueled by a flood of American soldiers returning from WWII’s European and Pacific theaters, the GI Bill sparked an explosion in college enrollment that continues to this day.
In 1940, fewer than one in twenty Americans had a college degree. Now it’s better than one in four[1]. Fueled by a flood of American soldiers returning from WWII’s European and Pacific theaters, the GI Bill sparked an explosion in college enrollment that continues to this day.
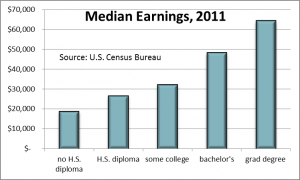
Higher education boosts productivity and pay. The earnings gap between those with and those without a college degree is dramatic. According to the Census, individuals 25 or older with bachelor’s degrees earned nearly $22,000 per year (80%) more than those with only a high school diploma.
But what does college cost?
College pricing rivals health care in opacity—most students receive some form of “aid.” Just as in buying a car, few pay the “manufacturer’s suggested retail price.” Bloomberg Businessweek reports that 94% of students in NYS private colleges & universities receive some form of financial aid[2]. Even in public colleges, two-thirds receive aid (in addition to the outright state support to the institution).
The College Board conducts an annual survey and reports that published tuition grew 52% from 96-97 to 11-12 while tuition net of aid (including federal tax credits) rose 22% over the period, suggesting that colleges and universities are increasing the “sticker price” at the same time that aid is also rising.[3] Using the College Board’s figures on net tuition and fees, students beginning four year degrees in 2011 will pay an average of $52,000 in tuition over four years in private schools and about $10,000 in public schools. Many pay more and many pay less, of course. Consider, too, the cost of room and board—another $35-40,000—and foregone earnings. Read more »
 Anybody who has followed the local government consolidation issue knows the difficulty of enacting significant, large-scale change. Old habits die hard, so it is no surprise that the procedural challenges to municipal restructuring are often daunting. Ever powerful are the inertia of the status quo and the “leap of faith” required on the part of voters to be convinced it’s possible to get to greener pastures.
Anybody who has followed the local government consolidation issue knows the difficulty of enacting significant, large-scale change. Old habits die hard, so it is no surprise that the procedural challenges to municipal restructuring are often daunting. Ever powerful are the inertia of the status quo and the “leap of faith” required on the part of voters to be convinced it’s possible to get to greener pastures.